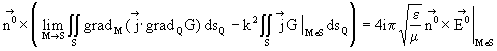|
The base of EDEM is formed by algorithms which were obtained as the result
of development of the principles suggested by the authors for solving the problems
under consideration. The detailed description of this technique one may be found
in [1,2].
In the current version of the program algorithms for solving the six types
of problems are realized. These are plane two-dimensional problems for two kinds
of polarization, a problems for surfaces of revolution with axisymmetric excitation;
three-dimensional problems for structures of arbitrary shape, and also a problems
for surfaces of revolution in which the incident field can be presented by quickly
converging Fourier series by azimuthal coordinate.
The original problem is formulated as rigorous integral equations of first
kind for surface current density induced on the analyzed structure by incident
electromagnetic field. In case of three-dimensional problem the integral equation
is |
|
|
Tasks of other five classes are reduced to the one-dimensional integral equations
or systems of such equations which have been written by a contour of cross-section
of analyzed surfaces.
Kernels of the equations by the special representation for scalar potential
are transformed to a form allowing subsequently greatly to reduce quantity of
calculations. As a result of the numerical solution of the equations there are
components of the currents induced on researched structure. Then various characteristics
of the electromagnetic fields resulting from these currents are calculated
For the numerical solution it can be used both constant approximation, and
the basic functions of higher order known as RWG functions.
For the solving of systems of linear algebraic equations both direct and iterative
methods are realized, in particular the Generalized Minimal Residual Algorithm
(GMREZ).
Besides the solving of the rigorous integrated equations, an approximate solving
of tasks on the basis of a method of physical optics is possible. The sizes of
researched structures can be at this very large.
-
Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1984, v.276, N 1, p.96-100.
-
Journal of Communications Technology and Electronics, Vol.45, Suppl.2, 2000, pp.S247-S259. |